The Link Between Iron Deficiency and Tinnitus: Understanding the Connection

It's estimated that about 15% of the worldwide population has some form of tinnitus, making it a common auditory trouble.
In this article, we take a look at a potential connection to low iron tinnitus. While tinnitus will have numerous reasons, including publicity to loud noise, ear infections, and age-associated hearing loss, latest research have revealed the intriguing link among iron levels inside the body and the tinnitus symptoms.
What is tinnitus?
Tinnitus is a regarded auditory phenomenon characterized by means of the belief of sound in the ears or head in the absence of any outside supply of sound. This state is frequently defined as a persistent ringing, humming, hissing, or maybe roaring noise. Also, a few people notice that their tinnitus increases or changes in pitch or tone after they move their head, jaw, or neck. The variations in tinnitus sound with head or jaw movement are often attributed to the complex nature of the auditory system. Tinnitus can be associated with issues in the inner ear, the auditory nerve, or the mind's auditory processing centers. Tinnitus is not a disease in itself, but rather a symptom of an underlying trouble, and it could arise in numerous instances. The sounds of tinnitus may be non-stop or intermittent, and they may intrude with normal life, inflicting sleep disturbances, attention difficulties, and heightened stress levels.
What is iron deficiency?
Let's discover what iron deficiency is. Iron deficiency is a common dietary disease characterized by an insufficient amount of iron within the body to meet its physiological desires. Iron is a vital mineral that performs a critical position in many biological procedures, most significantly inside the formation of hemoglobin.Hemoglobin is a protein located in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returns carbon dioxide to the lungs for exhalation. When the body lacks an adequate delivery of iron, it may cause numerous health problems.
Iron-deficiency anemia: This is one of the maximum common outcomes of iron deficiency.
Cognitive and behavioral changes: Iron deficiency can result in cognitive impairment, affecting memory, attention, and mental alertness.
Hair and Nail Problems: Individuals with iron deficiency may additionally experience modifications in the texture and appearance of their hair and nails. Hair might also become brittle, and nails may additionally increase ridges or come to break effortlessly.
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): Iron deficiency is a known danger factor for RLS, a neurological ailment which is characterized by an irresistible desire to move the legs, which is often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations.
Common causes for iron deficiency include:
Not enough dietary intake: Not consuming sufficient iron-wealthy meals, specifically in diets missing meat, fowl, or fish.
Blood loss: Chronic blood loss because of conditions along with gastrointestinal bleeding, heavy menstrual periods, or bleeding disorders.
Poor iron absorption: Certain clinical conditions, like celiac sickness or inflammatory bowel illnesses, can intrude with the frame's capacity to take in iron from the nutrition.
Increased iron needs: Infants, growing youngsters, pregnant women, and athletes may additionally require extra iron to guide their increased physiological needs.
The link between iron deficiency and tinnitus
Recent research has revealed a compelling connection between iron deficiency and tinnitus, showing the potential mechanisms that tie those two seemingly unrelated conditions collectively. The information received so far indicates a connection that deserves attention.
- Reduced oxygen supply to auditory system:
- Neurological impacts:
- Inflammatory processes:
- Cochlear hair cell vulnerability:
- Emotional distress:
One of the primary ways in which iron deficiency may additionally contribute to tinnitus is with the aid of reducing the oxygen delivered to the auditory system. Iron is a critical component of hemoglobin, the protein liable for sporting oxygen in red blood cells. When iron levels are low, hemoglobin manufacturing decreases, resulting in reduced oxygen-carrying capability inside the blood.
This diminished oxygen delivery could have detrimental outcomes on the delicate structures within the auditory system, including the hair cells inside the cochlea and the auditory nerves. Insufficient oxygenation can lead to cellular damage or dysfunction, potentially leading to tinnitus.
Iron is critical for proper brain function, and iron deficiency can have neurological results. Some researchers suggest that iron deficiency may affect the central auditory processing centers in the brain. Altered neural processing of auditory signals could contribute to the development or intensification of tinnitus symptoms.
Iron deficiency can lead to increased systemic inflammation in the body. Inflammation is known to play a role in a variety of health conditions, including those related to the auditory system. Increased levels of inflammation can affect the auditory pathways, potentially contributing to tinnitus.
Iron also performs a protecting function in maintaining the fitness of cochlear hair cells within the internal ear. These hair cells are responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound. Iron deficiency may make those cells extra at risk of damage or degeneration that potentially result in tinnitus.
Living with tinnitus may be distressing, and while mixed with the signs and symptoms of iron deficiency, it could contribute to heightened emotional stress and tension.
Addressing iron deficiency and tinnitus
If you suspect a link among iron deficiency and your tinnitus symptoms, taking proactive steps to deal with iron deficiency may be a critical part of handling and probably alleviating tinnitus.
Comprehensive blood test:
Ferritin is a protein that stores iron in the body, and measuring it could help diagnose iron deficiency. Your medical doctor will interpret the outcomes to determine when you have iron deficiency.
Iron-rich diet:
If you are diagnosed with iron deficiency, your doctor may propose nutritional adjustments to grow your iron intake. Include iron-wealthy foods on your eating regimen, such as red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, fortified cereals, spinach, and iron-fortified bread.
Monitor symptoms:
Keep song of both your tinnitus symptoms and any changes in iron levels. It may also take the time for iron levels to normalize.
Protect your hearing:
To prevent in addition hearing damage and worsening of tinnitus, defend your ears from loud noises with the aid of using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in noisy environments.
Supplements:
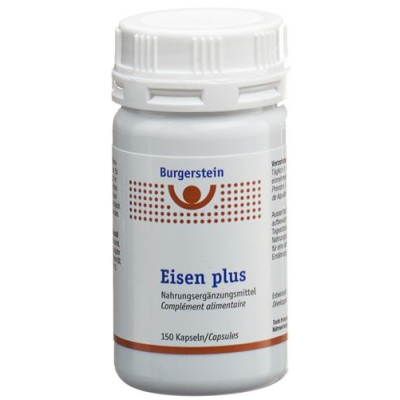
Iron dietary supplements can potentially assist with tinnitus if iron deficiency is a contributing issue to the condition. Iron dietary supplements are especially designed to raise iron stages in the frame. By addressing the underlying deficiency, they are able to potentially alleviate tinnitus signs and symptoms, which can be related to inadequate iron. Burgerstein Iron Plus Kaps is a dietary supplement designed to address iron deficiency. It also facilitates to lessen fatigue, contributes to the ordinary functioning of energy metabolism, also carries vitamins C, B and A and copper, without synthetic flavors, lactose unfastened, gluten unfastened and fructose unfastened.
Burgerstein iron plus kaps can 150 pcs
Burgerstein Eisen Plus is the ideal dietary supplement for a diet with little meat. Helps reduce fatigueContributes to the normal functioning of energy metabolismAlso contains vitamin C, B vitamins vitamin A and copperWithout artificial flavorsLactose free, gluten free and fructose freeWithout granulated sugar Application It is recommended to take 1 Burgerstein Eisen Plus capsule daily with some liquid. ingredients Soybean oil, edible gelatine (beef, pork), calcium L-ascorbate, ferrous fumarate, humectant (glycerol), calcium dpantothenate, emulsifier (lecithins (soy)), copper gluconate, pyridoxine hydrochloride, thiamine mononitrate, riboflavin, retinyl palmitate, peanut oil, coloring (iron oxides and ferric hydroxide), pteroylglutamic acid, cyanocobalamin..
52.21 USD
Understanding the position of iron in hearing health and its connection to tinnitus empowers people to take proactive steps towards dealing with these situations effectively. With continued research, it is becoming increasingly clear that correcting iron deficiency can play a critical role in the treatment of tinnitus symptoms. Using a comprehensive approach that includes dietary adjustments, medical evaluation, and individualized treatment plans, tinnitus sufferers can find relief and improve their quality of life.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
M. Wüthrich